Import Specifications (import spec) are created to load external data sources into the database. Data mapping and functionality to manipulate data are added to the import spec to ensure the data in the external data source meets the business rules for data input into the database.
An import spec allows the user to map data to the relevant entity using from the following different files:
On completion of the import spec the external source data is imported into the data load table and the records matched and processed as outlined in Matching Rules and Process Data Load Records.
Creating an Import Spec
Open the Import Specification search form by clicking on the Data Loads and Tasks icon on the Simplicity toolbar.
Click on the "Add Import Specification" icon in the search form
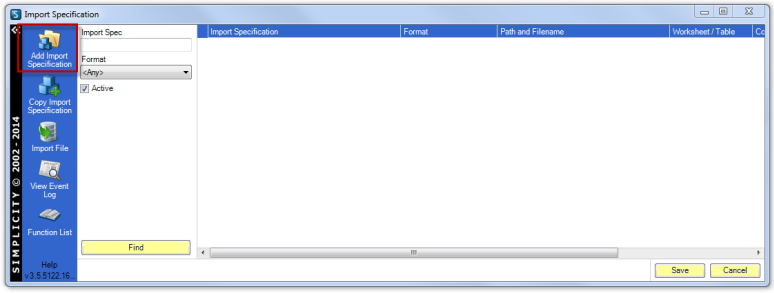
Enter a relevant name into the Name field.
Select the file format of the data to be imported.
Select the file location of the file to imported by clicking on the folder icon next to the File field.
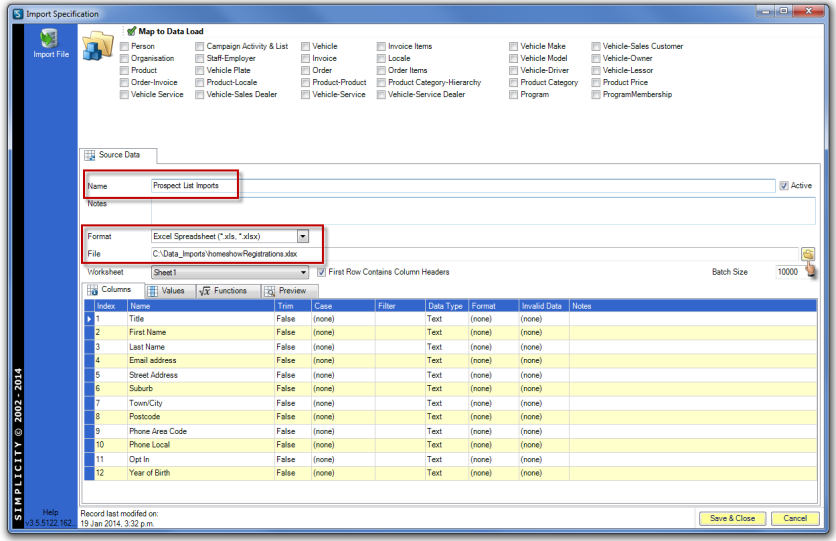
If required, set the "Trim" to "True" for each column and select the "Case" for each column, where relevant.
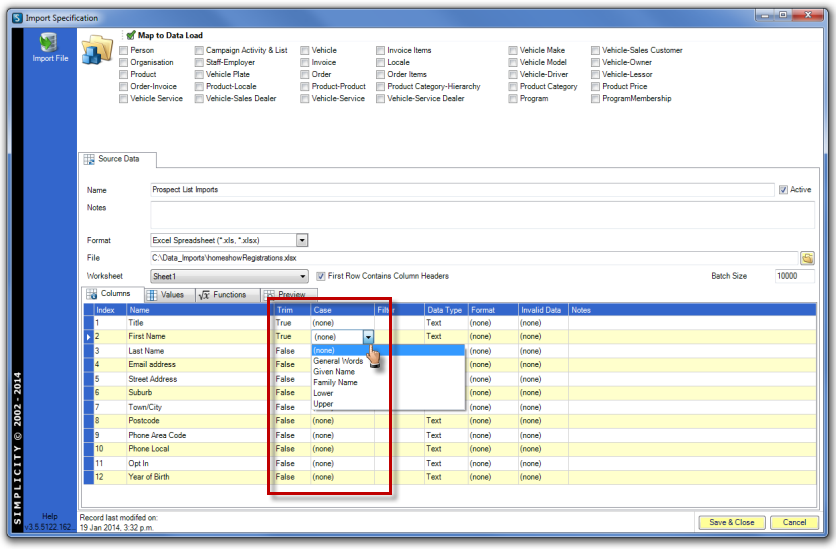
Click on the "Functions" tab in the Source Data screen to add functions.
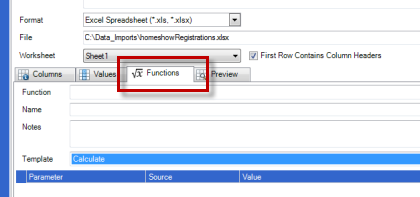
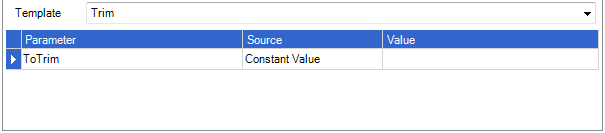
Add the function name to the name field and select a function from the template options by clicking on the down arrow. The appropriate parmeters will appear depending on the function template selected.
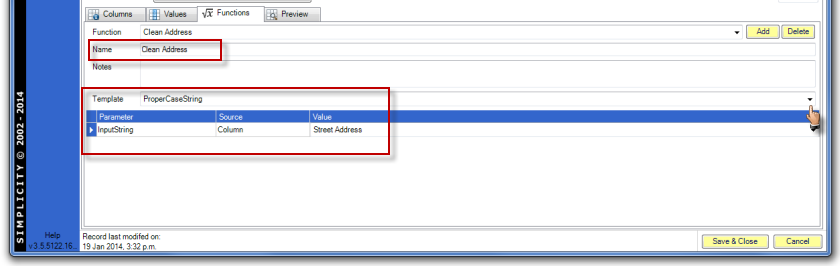
Select one of the three source options from the drop down menu —
Column: column heading from external data source.
Function: a function already added to the import spec.
Constant Value: enables user to enter text into the Value field.
After the Source option has been selected, choose the options available in the drop down menu, or enter text in the Value field.
Click the Add button next to the Function field to apply the function to the Import Spec.
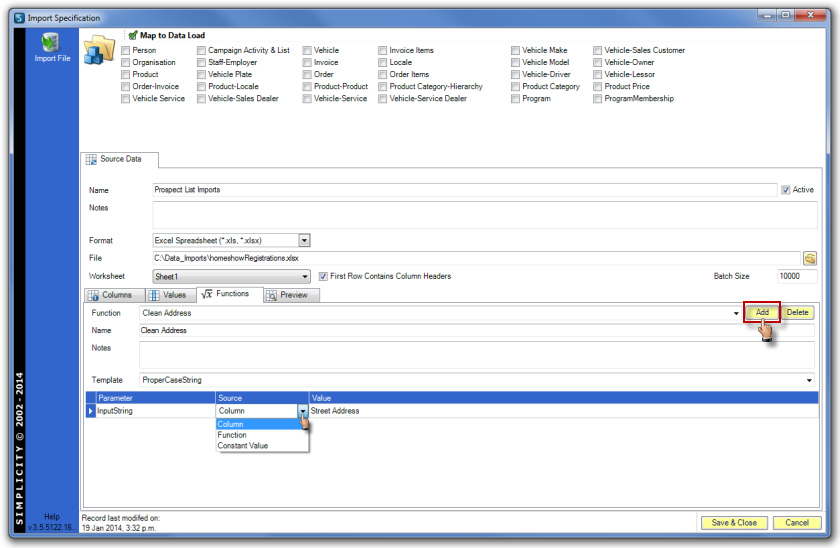
Map to Data Load Entity
After all functions have been added to the import spec select the appropriate entity data load table(s) under Map to Data Load in the top right of the Import Specification workspace. The number of options available will depend on the number of entities and relationship tables you have in your database.
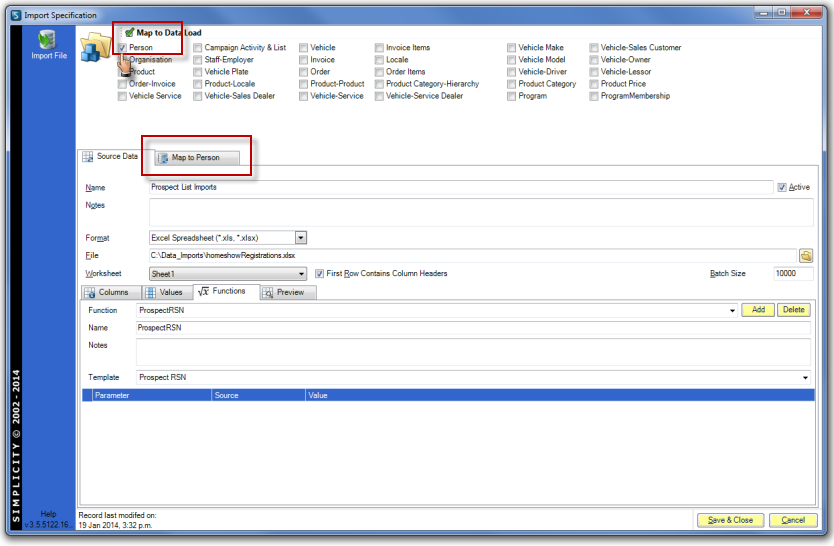
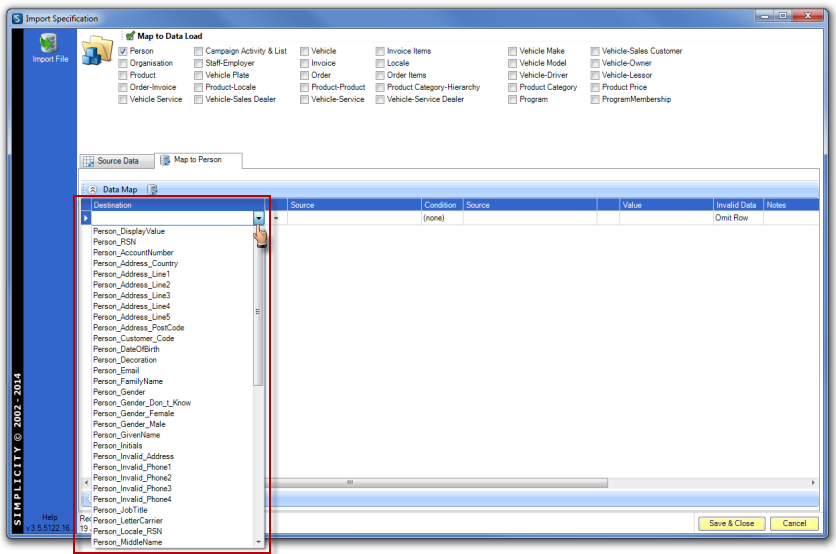
Click on the "Map to ..." tab. Right click in the white space and select Add Data Map. Select the Destination data load table field name from the drop down options.
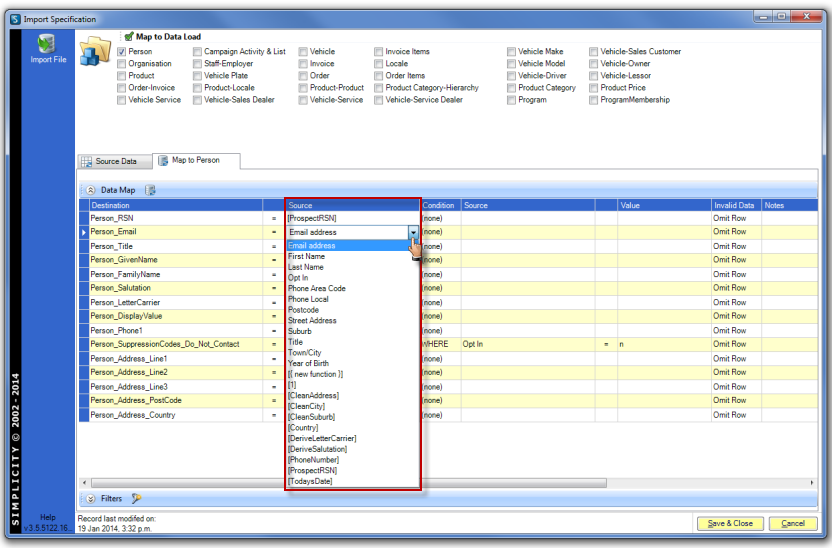
Select the appropriate function or external data source column name from drop down menu in the Source field. Add conditions to data if required.
Repeat the above process until all data load fields being used for this data load process have been mapped.
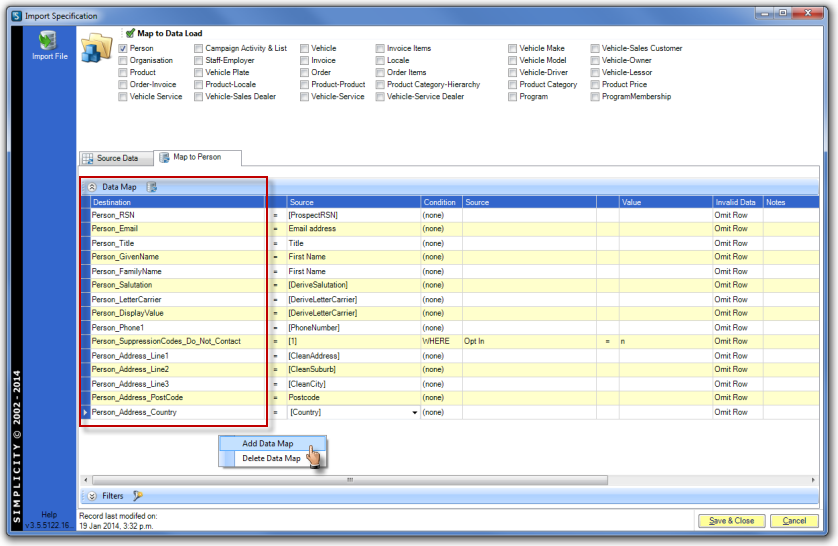
NOTE: Save and closing the import spec at various times during the creation of the import specification is recommended.
Import File
After data load tables and fields have been mapped the external data source is ready to be imported into the data load table(s).
Click on the Import File icon in the top left corner of the Import Specification workspace.
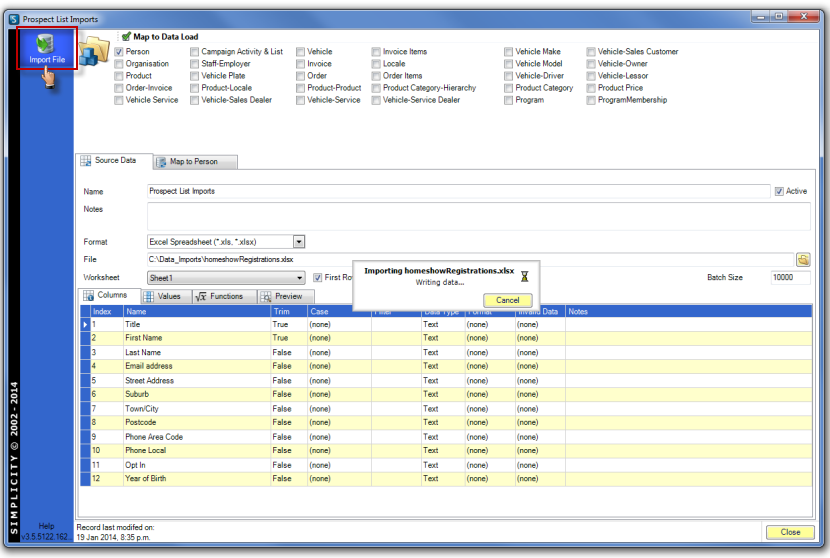
Click OK when prompt appears to signal the data has been imported successfully into the data load table(s).
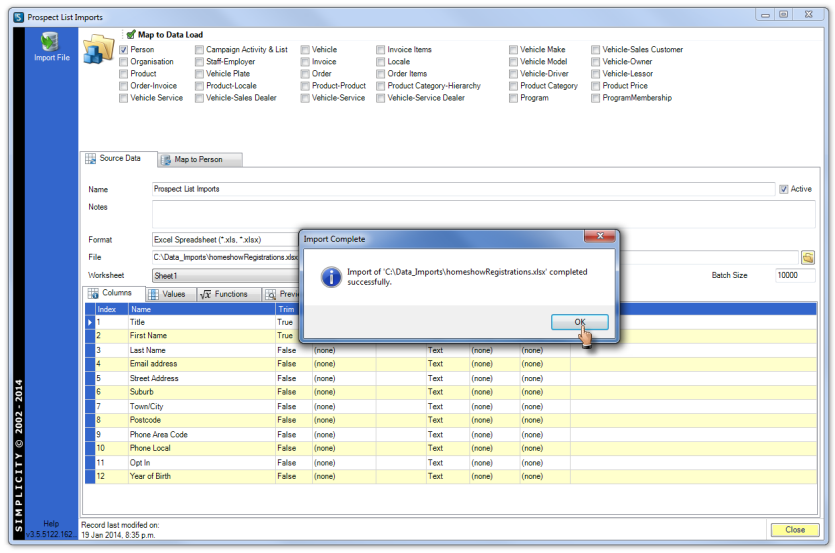
Load Data into Database
Check the data in the data load table(s) by opening the data load table(s) from the Simplicity Toolbar.
Select the source file — the file name of the external data source — from the drop down options from the Source field and click Find. Scroll across the table fields and check the data in the data load columns has been loaded as expected.
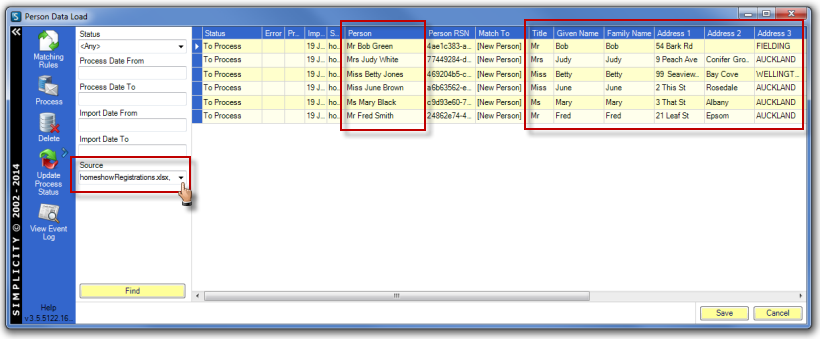
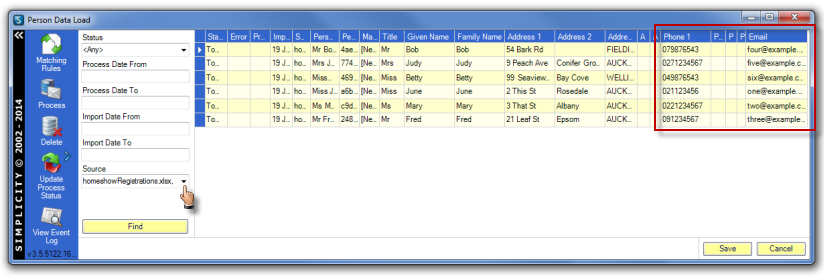
Run the match rules as outlined in Matching Rules before processing the data as outlined in Process Data Load Records.
Import Spec Functions
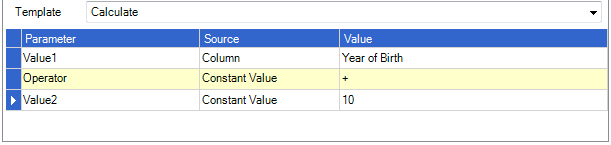
Calculate
Performs the mathematical operation between value 1 and value 2 and returns the result.
Valid operators are + , - , * , / , ÷
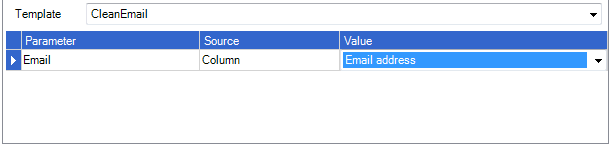
Clean Email
Returns the email address with all leading and trailing white space removed.
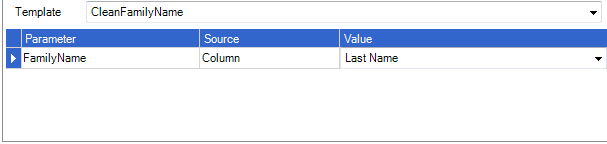
Clean Family Name
Returns the family name in a proper case format taking into account Simplicity family name formatting rules for example: mcdonald = McDonald, o'brien = O'Brien. The family name also has all leading and trailing white space removed.
Clean Gender
Returns the gender as 'Male' or 'Female'. Priority is given to the gender field where this is already populated with ('M', 'Male', 'F'. 'Female'). Where no gender is specified it looks up Simplicity gender naming rules and tries to determine, firstly from the title, secondarily from the given name and lastly from the middle name, where their name successfully denotes their gender. For example: Mr Chris James Smith = Male (derived from title), Chris James Smith = Male (derived from middle name), Chris Smith = Undetermined (no match found).
Clean Given Name
Returns the given name in a proper case format taking into account Simplicity given name formatting rules for example: geoff = Geoff, SALLY = Sally. The given name also has all leading and trailing white space removed.
Clean Invalid Email
Returns True (1) or False (0) as to whether the email address is determined to be invalid. An email address is determined to be invalid where the email address has a value supplied and the email address does not contain an '@' or '.' For example: blank = 0, sales@example.org = 0, www.example.org = 1, sales@example = 1
Clean Letter Carrier
Returns a letter carrier formatted in the following pattern: { Cleaned Title } { Capitalised First Initial of Given Name } { Capitalised First Initial of Middle Name } { Cleaned Family Name }. Where no title and no given name is specified or the resulting letter carrier is less than three letters long then no result is returned. For example: chris james mcdonald = Mr C J McDonald, chris mcdonald = C McDonald, james mcdonald = Mr J McDonald, sally jane mcdonald = Ms S J McDonald, mrs sally mcdonald = Mrs Sally McDonald, sally = blank
Clean Phone Ext
Returns the extension portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Clean Phone IDD
Returns the IDD (International Direct Dialing) portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Clean Phone Invalid
Returns True (1) or False (0) as to whether the phone number is determined to be invalid. A phone number is determined to be invalid where the phone number consists only of numbers and the phone number is less than six digits long.
Clean Phone Local
Returns the local portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Clean Phone STD
Returns the STD (Subscriber Trunk Dialing) portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Clean Salutation
Returns a salutation. The function will return the cleaned given name but where the given name has not been specified it will return a salutation formatted in the following pattern: { Cleaned Title } { Cleaned Family Name }. For example: chris james mcdonald = Chris, chris mcdonald = Chris, mr j mcdonald = Mr McDonald, sally jane mcdonald = Sally, mrs mcdonald = Mrs McDonald, sally = Sally
Clean Title
Returns a title. The function will return the title but where the title has not been specified it will check the specified gender and return the default title for the gender. If this is indeterminate then the title is checked from the gender evaluation of the given name, where this is indeterminate the title is checked from the gender evaluation of the middle name. For example: chris james mcdonald = Mr, chris mcdonald = blank, mr j mcdonald = Mr, sally jane mcdonald = Ms, mrs mcdonald = Mrs, sally = Ms
Clean Website
Returns the website with all leading and trailing white space removed.
Clean Website Invalid
Returns True (1) or False (0) as to whether the website is determined to be invalid. An website is determined to be invalid where the website has a value supplied with 3 or more letters and the website does not contain an '.' For example: blank = 0, www.example.org = 0, ww = 1, sales@example = 1
Compare Value
Performs the comparison between 'Value to Check' and 'Compare To' and returns the 'Return If True' value if the comparison is true and returns the 'Return If False' value if the comparison is false.
Valid operators are > , >= , = , <= , < , <>
Concatenate
Returns a result in the following format where a seperator is supplied: { Value 1 }{ Seperator }{ Value 2 }
Where a seperator is not supplied the following format is used: { Value 1 }{ Value 2 }
Both value 1 and value 2 must be specified for a concatenated value to be returned.
Constant Value
Returns the value specified.
Contains
Checks whether the 'Find Expression' value can be found in the 'In Expression' value. The 'Return If Found' value is returned if it was found and the 'Return If Not Found' value if it was not found. If no 'Return If Found' value is specified then the value of 1 is used. If no 'Return If Not Found' value is specified then the value of 0 is used. The search is case sensitive.
Date Diff
Returns the difference between 'Date 1' and 'Date 2' for the interval you specify.
If 'Date 1' represents a later date and time than 'Date 2', a negative number will be returned.
The valid intervals are: Year, Quarter, Month, DayOfYear, Day, WeekOfYear, Weekday, Hour, Minute, Second
Derive Family Name From Full Name
Returns the family name from the full name specified in the 'Input String' using the Simplicity name functions. If the family name is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Derive Gender
Returns the gender as 'Male' or 'Female'. It looks up Simplicity gender naming rules and tries to determine, firstly from the title, secondarily from the given name and lastly from the middle name, where their name successfully denotes their gender. For example: Mr Chris James Smith = Male (derived from title), Chris James Smith = Male (derived from middle name), Chris Smith = Undetermined (no match found).
Derive Given Name From Full Name
Returns the given name from the full name specified in the 'Input String' using the Simplicity name functions. If the given name is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Derive Letter Carrier
Returns a letter carrier formatted in the following pattern: { Cleaned Title } { Capitalised First Initial of Given Name } { Capitalised First Initial of Middle Name } { Cleaned Family Name }. Where no title and no given name is specified or the resulting letter carrier is less than three letters long then no result is returned. For example: chris james mcdonald = Mr C J McDonald, chris mcdonald = C McDonald, james mcdonald = Mr J McDonald, sally jane mcdonald = Ms S J McDonald, mrs sally mcdonald = Mrs Sally McDonald, sally = blank. If the letter carrier is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter. This method can also optionally have the decoration specified to be included in the derived letter carrier.
Derive Letter Carrier From Full Name
Returns the letter carrier from the full name specified in the 'Input String' using the Simplicity name functions. If the letter carrier is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Derive Middle Name From Full Name
Returns the middle name from the full name specified in the 'Input String' using the Simplicity name functions. If the middle name is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Derive Phone Extension
Returns the extension portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Derive Phone IDD
Returns the IDD (International Direct Dialing) portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Derive Phone Invalid
Returns True (1) or False (0) as to whether the phone number is determined to be invalid. A phone number is determined to be invalid where the phone number consists only of numbers and the phone number is less than six digits long.
Derive Phone Local
Returns the local portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Derive Phone STD
Returns the STD (Subscriber Trunk Dialing) portion of the phone as determined by the Simplicity phone number parsing rules.
Derive Salutation
Returns a salutation. The function will return the cleaned given name but where the given name has not been specified it will return a salutation formatted in the following pattern: { Cleaned Title } { Cleaned Family Name }. For example: chris james mcdonald = Chris, chris mcdonald = Chris, mr j mcdonald = Mr McDonald, sally jane mcdonald = Sally, mrs mcdonald = Mrs McDonald, sally = Sally. If the salutation is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Derive Salutation From Full Name
Returns the salutation from the full name specified in the 'Input String' using the Simplicity name functions. If the salutation is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Derive Title
Returns a title. The title is checked from the gender evaluation of the given name, where this is indeterminate the title is checked from the gender evaluation of the middle name. For example: chris james mcdonald = Mr, chris mcdonald = blank, mr j mcdonald = Mr, sally jane mcdonald = Ms, mrs mcdonald = Mrs, sally = Ms
Derive Title From Full Name
Returns the title from the full name specified in the 'Input String' using the Simplicity name functions. If the title is successfully determined then this can be optional cased using the Simplicity name casing routines by specifying 1 in the 'Case' parameter.
Index Of
Returns the 'Find Expression' position within the 'In Expression' value beginning at the specified start position. If no start position is specified it will begin the search from the beginning of the 'In Expression' value. The position the text is found is returned if it is found. If the text is not found then -1 is returned. The search is case sensitive and the text position is indexed from 0.
MP Address Match String
Returns a Simplicity address match string for the specified address lines.
Now
Returns the current date and time.
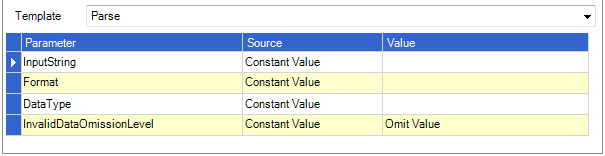
Parse
Converts the specified string representation of a date and time as specified in the 'Input String' parameter to its Date and Time equivalent using the specified format and culture-specific format information. The format of the string representation must match the specified format exactly. The 'Data Type' parameter should be set to 'Date'. The 'Invalid Data Omission Level' parameter has since been deprecated.
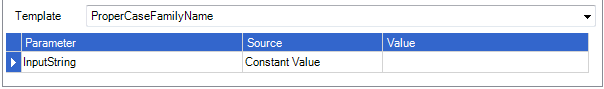
Proper Case Family Name
Returns the input string in a proper case format taking into account Simplicity family name formatting rules. A standard proper case is performed on the input string prior to passing it to the Simplicity family name formatting rules. For example: mcdonald = McDonald, o'brien = O'Brien. The family name also has all leading and trailing white space removed.
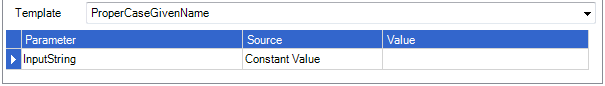
Proper Case Given Name
Returns the input string in a proper case format taking into account Simplicity given name formatting rules. A standard proper case is performed on the input string prior to passing it to the Simplicity given name formatting rules. For example: geoff = Geoff, SALLY = Sally. The given name also has all leading and trailing white space removed.
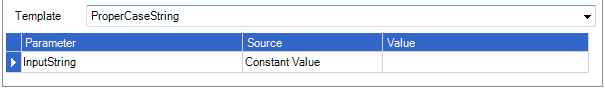
Proper Case String
Returns the proper case version of the supplied input string. Proper casing is also referred to as camel casing. For example: the quick brown fox = The Quick Brown Fox, THE LAZY DOG = The Lazy Dog
Prospect RSN
Returns the prospect RSN as defined for the entity data load you are processing.
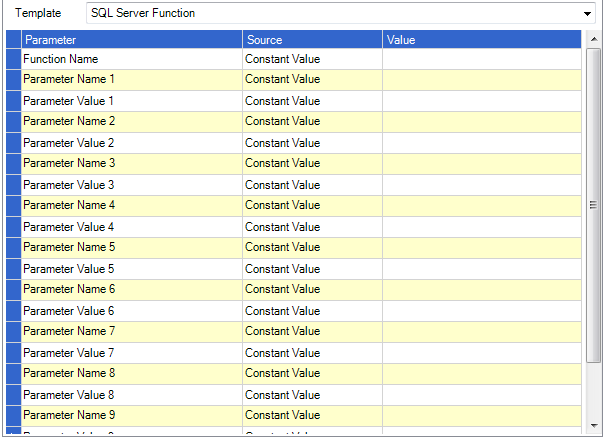
SQL Server Function
This will return a value from a system or custom sql server function. The function name should be entered in the following format { Schema }.{ Function Name } for example dbo.MySampleFunction. Up to 10 parameters can also be specified through the name/value pairs.
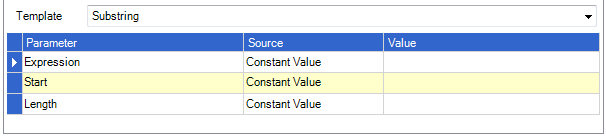
Sub String
Returns the portion of text within the 'Expression' value beginning at the specified start position for the number of characters as specified in the 'Length' parameter. If no length position is specified it will include all characters from the start position until it reaches the end of the 'Expression' value. The first character's position is 0.
To Lower
Returns the input string as lower case. For example: HELLO WORLD = hello world, Hello World = hello world
To Upper
Returns the input string as upper case. For example: hello world = HELLO WORLD, Hello World = HELLO WORLD
Trim
Returns the to trim value with all leading and trailing white space removed.